
In class 11, we studied only Microeconomics
Economy: The Economy is an economic organisation which provides us with resources to earn a livelihood.
Important Questions about the Economy:-
Que. What is the economic problem, and why does it arise?
Ans. The economic problem is mainly about the problem of choice among scarce resources, which means, in every economy, human beings have unlimited wants but the resources to satisfy them are limited, and these resources have alternative uses; therefore, the problem of choice arises, and this problem is known as the economic problem.
Economic problem arises because of the following three factors :
- Human wants are unlimited: some human wants are recurring in nature, whereas some wants arise due to social and economic factors like an increase in income, changes in taste and Preferences, etc.
- Scarce resources: The resources available in the economy are limited in supply as compared to their demand.
- Alternative uses of resources: The resources available in the economy can be put to alternative uses. For example, steel can be used for manufacturing machinery, automobiles, etc.
Que. Discuss the central problem of an economy.
Ans. Every economic system, whether it is capitalist, socialist or mixed, has some basic economic problems. These are called the central problems of an economy. An economic problem is defined as the problem of decision-making or the problem of choice in order to allocate the available resources efficiently in producing activities to satisfy human wants.
The central problems of an economy are categorised as follows:
Problem of allocation of resources: It is the basic problem related to the utilisation of resources for the production of different goods and services.
The following are the problems relating to the allocation of resources :
(i) What to produce, and what in quantity: It is defined as the problem of choice between different commodities that can be produced from a given scarce resource. This problem arises because of alternative uses of scarce resources. The choice made is on the basis of various social and economic factors. So every economy has this problem that what to produce and in what quantities. It has two dimensions :
a. Kinds of goods to be produced
b. Quantity of goods to be produced.
For example, an economy has to choose between consumer goods and capital goods. A developed economy can give more preference to consumer goods as it has to maintain the level of infrastructure already developed. On the other hand, a developing economy will give more preference to capital goods to increase the level of production and growth rate in the economy.
(ii) How to produce? It is defined as the problem of choice between different techniques of production that can be used in the production of different commodities, so that the given resources are utilised to their maximum efficiency. It arises due to the availability of an alternative technique of production.
In this, two types of techniques of production techniques are to be used for production :
a. Labour Intensive Technique: The technique which uses more labour and less capital is known as a labour-intensive technique.
b. Capital Intensive Technique: The technique which uses more capital and less labour is known as the capital-intensive technique.
For example, in economics, a 100-meter cloth is produced by spending 1000rs. on labour and 500rs. In the capital, it is a labour-intensive technique. On the other hand, if a 100-meter cloth is produced by spending 200rs. on labour and 800rs. On capital, then it is a capital-intensive technique. From both the techniques, the capitalist economy will select the capital-intensive technique as the cost of production is 1000rs. On the contrary, an economy where labour is abundant compared to capital will prefer to use labour-intensive techniques as it wants to give more employment to people.
(iii) For whom to produce: This problem is related to the distribution of income or output in the economy. Thus, this problem has two aspects :
a. Personal distribution: It means how the national income of an economy is distributed among different groups of people, like the rich or the poor.
b. Factorial distribution: It refers to the returns of factors of production in the total national income of an economy. Like rent, wages, interest and profits.
Que. Explain the concept of the economising of resources?
Ans. In economics, economising means making the optimum use of available resources. As human wants are unlimited and resources are limited so an economy needs to economise the available resources. In order to make the optimum use of what is available, the society and individuals must make choices. Every individual and society has to choose which wants they should satisfy by making use of scarce means which have alternative uses.
Que. What is Economics?
Ans. Economics is the study of how individuals and society make choices in the presence of scarcity of resources and how levels of national income and employment are determined, and what determines their growth.
Que. What is the wealth definition of Economics?
Ans. According to the father of Economics, Adam Smith, “Economics is an enquiry into the nature and causes of the wealth of a nation”. So, according to this definition, the study of economics enables us to know what wealth is, how the volume of wealth can be increased and what factors determine the saving and investment for economic development.
Que. Define scarcity.
Ans. Scarcity is a stock of resources being available in insufficient amounts relative to the amount desired at a particular point in time. In other words, when the demand for resources is greater than the supply of resources, then it is known as scarcity.
Demand of Resources > Supply of Resources
Que. Explain the concept of the Production Possibility Curve with the help of a diagram.

Ans. The Production Possibility Curve may be defined as a curve which represents various possible combinations of two commodities that can be produced with fuller utilisation of given resources and technology in an economy. It is also known as the Production Possibility Frontier because it represents the maximum quantity of two commodities that can be produced with the help of a given resource, so that no economy can operate outside the Production Possibility curve.
Production Possibility curve is based on the following assumptions:-
a. The amount of productive resources available in the economy is fixed and transferable.
b. Only two commodities can be produced from the given amount of resources.
c. There is no change in technology used in the production process.
d. All the resources are fully and efficiently employed.
e. The given resources are not equally efficient in all productive activities.
Que. Explain the properties of the Production Possibility Curve.
Ans. Properties of PPC:-
It slopes downwards: The Production Possibility Curve slopes downwards from left to right. PPC is based on fuller and efficient utilisation of resources and hence represents the maximum production level that can be achieved. Therefore, the production of one commodity can be increased only by transforming the resources from another commodity, i.e., by reducing the production of another commodity. The output of both goods can’t be increased simultaneously because resources are already being fully utilised. So to increase the production of one commodity, the economy has to sacrifice the production of another commodity.
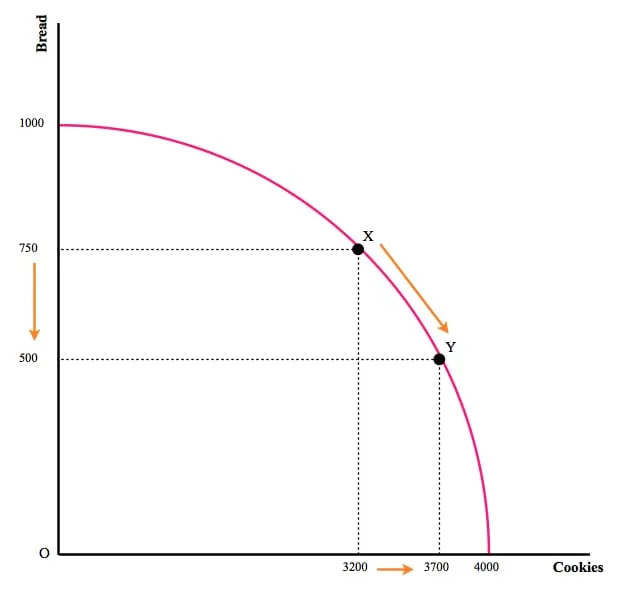
- It is concave to the origin: The Production Possibility Curve is concave to the origin, which is based on the concept of increasing marginal rate of transformation. When the resources are withdrawn from one commodity to increase the production of another commodity, the marginal rate of transformation increases, i.e., MRT increases.
Reasons for increasing MRT/MOC :
(i) Resources are not equally efficient in the production of all commodities.
(ii) The Law of Diminishing Returns applies.
Que. Explain the shift in the production possibility curve.
Ans. Production Possibility can shift in the following ways :
(i) Upward shift of PPC: PPC shifts to the right or upward from its existing position if resources, i.e., skilled labour, capital goods, and better technology, increase. Shift in PPC shows that the production of both goods has increased. It is an indicator of the growth of resources.
(ii) Downward shift of PPC: PPC never shifts towards the left, but it is only possible when there is a decrease in resources due to large-scale natural calamities, i.e., earthquake, flood, or war etc. But it is a rare possibility. Sometimes, if any of the resources decrease or are destroyed, then only a point inside lies, not the PPC entirely shifts.

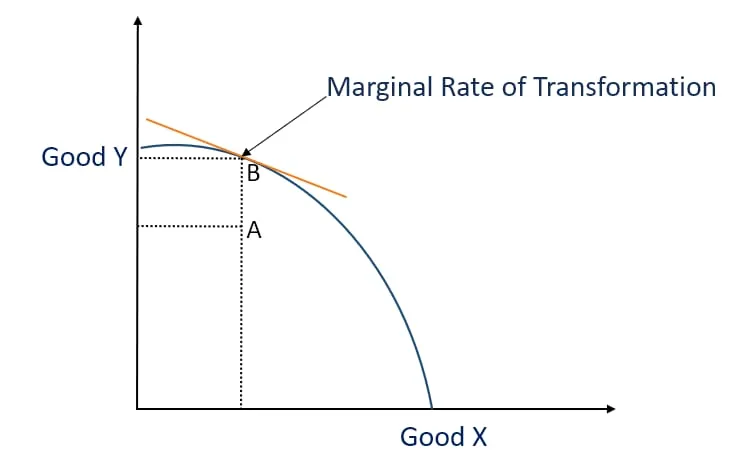
Que. What is the Marginal Rate of Transformation? How does it affect PPC?
Ans. Marginal Rate of Transformation (MRT) is the ratio of the number of units of a good sacrificed to increase one more unit of the other good. MRT can also be called the Marginal opportunity cost. It is defined as the additional cost in terms of the number of units of a good sacrificed to increase an address unit of the other good.
MRT affects the PPC in the following way :
(i) If MRT increases, then PPC will be concave to the point of origin.
(ii) If MRT is constant, then PPC will be a downward-sloping straight line.
(iii) If MRT decreases, then PPC will be convex to the point of origin.
Que. What is opportunity cost? Explain it with the help of an example.
Ans. The opportunity cost of any commodity is defined as the cost of the next best alternative, which has been sacrificed for producing the given commodity. For example, on a piece of land, a farmer can produce 50 kg. of wheat by using a given quantity of inputs. He can also produce 40 kg of rice with the same amount of resources. Here, the opportunity cost of producing 50 kg. of wheat is 40 kg of rice.
Que. Define Microeconomics.
Ans. The term micro in the English language has been derived from the Greek word ‘Mikros’, which means ‘small’. Microeconomics is that part of economic theory which deals with the individual parts of a system. It is also called “price theory”.
Que. Define Macro Economics.
Ans. The term macro in the English language has been derived from the Greek word ‘Makros’, which means ‘large’. Macroeconomics is the branch of economics that studies the overall performance and behaviour of an economy as a whole, focusing on aggregate indicators like GDP (Gross Domestic Product), inflation, economic growth, and unemployment.
Important MCQs of Consumer Equilibrium - Class 11th
Contact us at news@eliyasphere.com for all chapter notes in a single PDF.

