Consumer Equilibrium
Consumer Equilibrium refers to a situation, when consumer spend his income in such a manner that he gets maximum satisfaction and he feels no urge to change.

Utility : Utility is a want satisfying power of a commodity.
- Utility vary from person to person.
- Utility vary from time to time.
- Utility vary from place to place.
- Utility is ethically neutral.
Total Utility : It is the sum of total Utility which is derived by consumer by consuming all units of a particular commodity.
[ TU = MU ]
Marginal Utility : It is the additional utility from consuming an additional unit of a commodity.
[ MUn = TUn – TUn-1 ]
Example, Total utility = 110
Total utility n-1 = 100
Solution; 110 – 100 = 10 utils.
Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility : According to this law, A consumer gets maximum when the price of a is equal to its marginal utility. As more and more unit of commodity bought, their marginal utility diminishes.
Assumption of Diminishing Marginal Utility (DMU) :-
- Utility must be measure
- Rational consumer
{Knowledge about satisfaction} - Income must be constant
- Quantity, Quality and Size of goods must be constant.
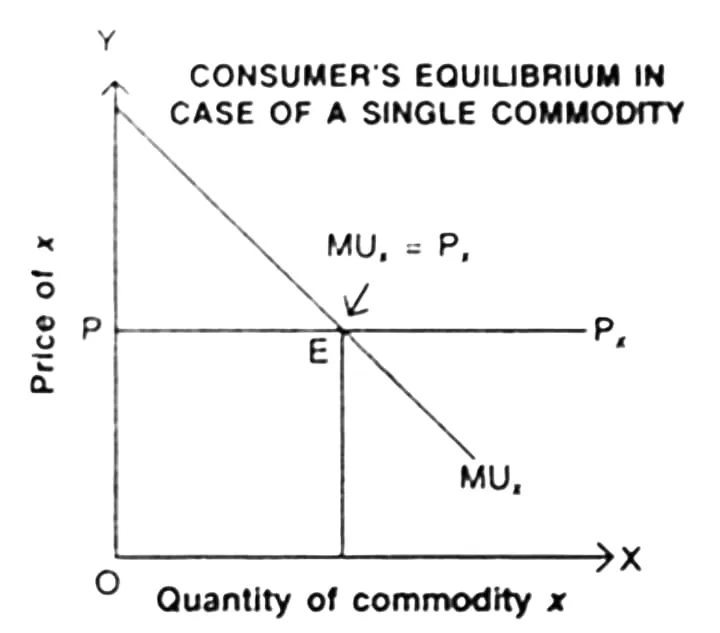
Consumer Equilibrium (In case of one/ single commodity) : In case of single commodity the consumer is in equilibrium at the quantity of units at which the marginal utility of good X is equal to price of good X.
Assumption :-
- Rational consumer.
- Marginal utility of money must be constant in this consumer equilibrium.
- Consumer must be continuous in consumption.
- Budget or Income of consumer must remain unchanged.
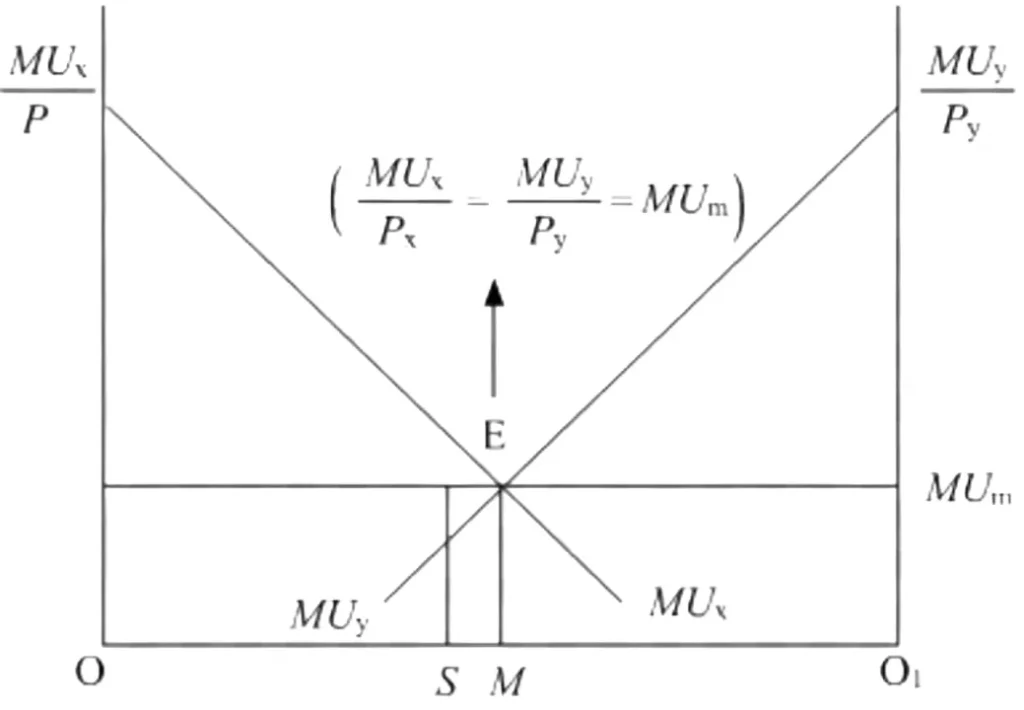
Consumer Equilibrium (In case of two or more commodity) : The consumer is said to be in equilibrium at a point at which the MU of money expenditure on both the goods are equal in symbol terms.
[ MUx/Px = MUy/Py ]
Consumer Equilibrium in case of two commodity is also known as :
“Law of equal marginal utility” and
“Law of maximum satisfaction”
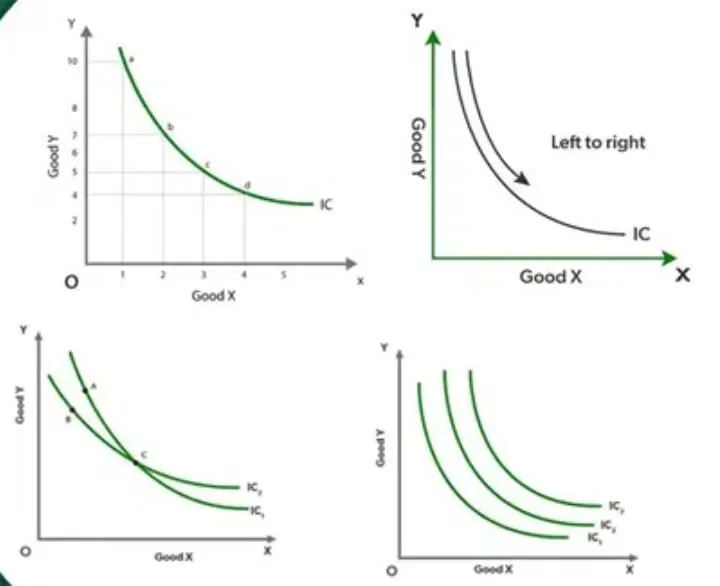
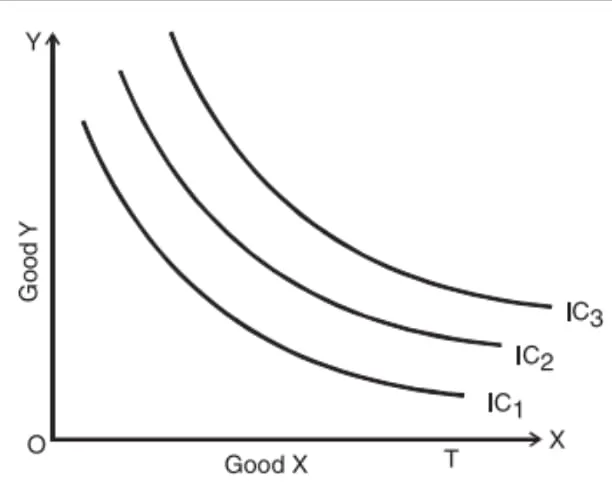
Indifference Curve (IC) : Indifference curve is an alternative combination of consumption of two goods which gives same level of satisfaction to the consumer.
Properties of IC :-
- Indifference Curve slopes downward : IC slopes downwards slope because to consume more of Good-X consumer must give up some units of Good-Y to remain on the same level of satisfaction.
- Convex to the origin : IC is strictly convex because of the assumption that MRS (Marginal Rate of Substitution) continuously falls as more of Good-X is consumed because of the operation of the law of Diminishing marginal utility.
- Indifference Curve can’t touch or intersect each other : Two IC can never intersect each other, if they would intersect, then at the intersect point, the satisfaction level would become same of the both the ICs. Whereas according to the definition of IC each point on a IC gives equal satisfaction but here all point on both the ICs are giving same satisfaction which is not possible.
- Indifference Curve gives higher level of satisfaction : Higher IC shows higher consumption. By assumption, higher consumption means higher utility.
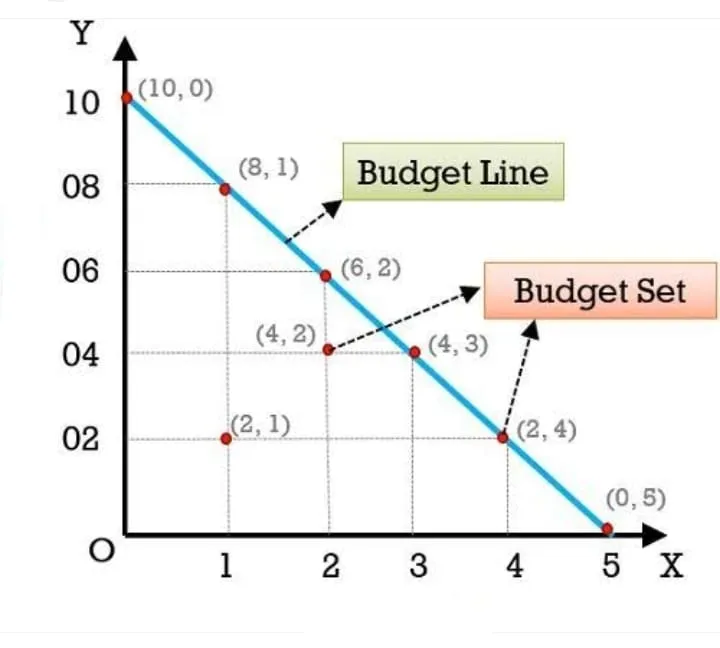
Budget set : The budget set is the collection of all the bundles of two goods that a consumer can buy with his Income at the prevailing market prices.
Budget line : A line which represents the alternative combination of the two goods with the given money income and price of two goods.
Equation of Budget line : [ PxQx + PyQy ]
Properties of Budget line :-
- Any combination below the budget line indicates that consumer is not spending his entire money.
- It slopes downward because additional unit of good-1 can only be purchased when good-2 to be buying less.
- Budget line is always a straight line as its slope is represented by the price ratio. As price ratio is constant throughout, The budget line is a straight line.
- Any combination outside the budget line is out of purchasing power to a consumer, It is unattainable for the consumer.
Important Questions of Consumer Equilibrium
Que. Define Indifference Map.
Ans. Indifference Map is a collection of Indifference Curves corresponding to different levels of satisfaction. Whereas an Indifference Curve represents the combination of providing a single level of satisfaction an indifference Map contains several indifferent curved which represents different levels of satisfaction. All the indifference curves taken together constitute the indifference Map of the consumer. Thus the map describes preference of the consumer.
Que. Explain the law of diminishing marginal utility with the help of schedule and diagram.
Ans. According to this law as more units of a good are consumed continuously and in standard units, the marginal utility derived from the consumption of every additional unit will keep diminishing. A consumer gets maximum satisfaction when the price of a commodity is equal to its marginal utility. As more units of a commodity are bought, their marginal utility diminishes.
Que. Explain assumption of consumer equilibrium.
- Rational consumer : Consumer is assumed to be rational. A rational consumer is one who is keen to get maximum satisfaction out of his limited income.
- Cardinal utility : Utility of every commodity can be measured in terms of cardinal numbers, such as 1, 2, 3, 4, etc.
- Independent Utility : It assumed that the utility that a consumer gets from a commodity depends upon the quantity of that commodity. It is not affected by the utility derived from other goods.
- Marginal utility of money is constant : It is assumed that money measures the marginal utility of a commodity; as such, its own marginal utility should remain constant so as to service as an ideal measure.
- Fixed income and price : Another assumption of this analysis is that the income of the consumer and the commodity price remain fixed.
- Tastes and Preferences : Tastes of the consumer also remain unchanged. The term taste is used in a broad sense so as to include in it, the impact of personal likes and dislikes, trends and fashions, as well as the effect of the weather.
- Perfect Knowledge : The consumer knows the different goods on which he can spend his income and how much utility he is likely to get out of the expenditure.
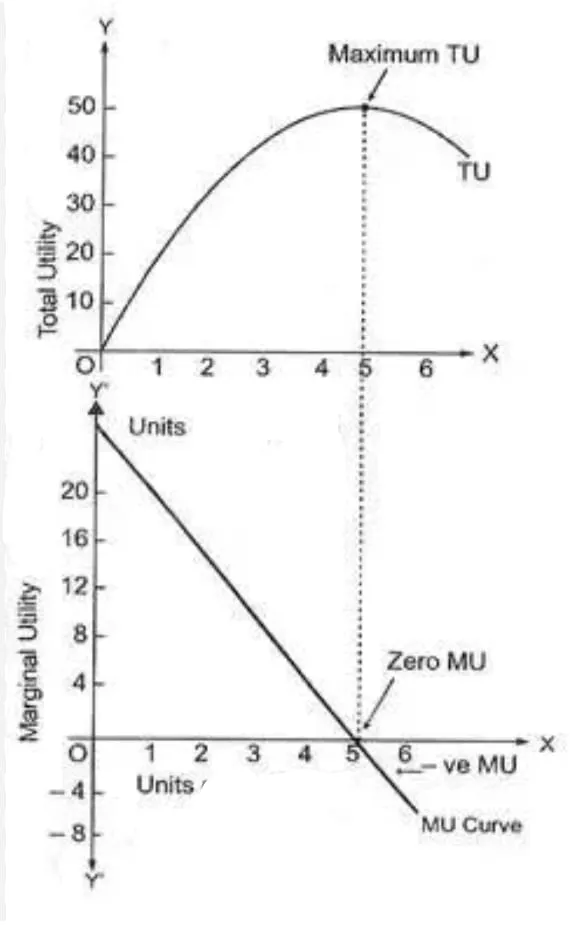
Que. Define relationship between TU (Total Utility) and MU (Marginal Utility) in consumer equilibrium
Ans. Relationship between TU & MU in consumer equilibrium :-
(i) When TU increases at decreasing rate, MU decrease.
(ii) When the TU is maximum; TU cuts MU at their maximum point & MU becomes 0.
(iii) & When TU decreases at Increasing rate, MU becomes negative.
Important MCQs of Consumer Equilibrium - Class 11th
Contact us at news@eliyasphere.com for all chapters notes in a single pdf.


